Fidelity Bonds vs Surety Bonds: Understanding Key Differences
Fidelity Bonds vs Surety Bonds: Understanding Key Differences
At a Glance: Fidelity bonds and surety bonds protect businesses in very different ways. Fidelity bonds safeguard companies from internal threats such as employee theft or fraud, while surety bonds guarantee that contractors or licensed professionals meet their obligations to project owners, regulators, or the public. Choosing the right bond helps business owners avoid compliance issues and protect their financial interests.
In the complex world of business insurance, fidelity bonds and surety bonds can create confusion. Even though they’re both considered "bonds," these financial instruments serve fundamentally different purposes. Fidelity bonds protect businesses against employee dishonesty, including theft and fraudulent acts. Surety bonds protect project owners and government entities when contractors or businesses fail to meet their commitments.
For business owners, understanding who these bonds protect, the number of parties involved, how claims are processed, and when each type is required is essential for proper risk management and regulatory compliance. Choosing the wrong bond type or failing to secure adequate insurance coverage can expose your business to significant financial losses or prevent you from obtaining necessary licenses and contracts.
Understanding Fidelity Bonds
Definition and Purpose
Fidelity bonds function as specialized insurance that protects businesses against financial losses from employee theft, fraud, and dishonest acts. Unlike traditional insurance protecting against external threats, fidelity bonds address internal risks, such as the potential for employees to steal money, property, or sensitive information.
Fidelity bond coverage provides financial protection and serves as a deterrent to employee dishonesty. Coverage typically includes many different incidences that result in financial loss to the employer, including:
Theft of money, securities, and physical property- Forgery and alteration of financial instruments
- Computer fraud and electronic theft
- Embezzlement schemes
Types and Coverage
Fidelity bonds come in several configurations, including-
- Individual Bonds: These cover specific employees in positions of high trust.
- Blanket Bonds: These provide broader protection by covering all employees within an organization.
- Position Bonds: These offer coverage tied to specific job roles, automatically extending to whoever holds that position.
Many businesses opt for comprehensive commercial crime policies that include fidelity coverage alongside protection against other criminal acts.
Industries Requiring Fidelity Bonds
Certain industries face mandatory fidelity bonding requirements-
- Financial Services and Banking: These institutions must maintain fidelity coverage to protect customer funds and meet regulatory requirements.
- Investment Advisors: Fiduciaries managing client assets face bonding requirements under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA).
- Government Contractors: These professionals often must provide proof of fidelity bonding as a condition of contract awards.
- Healthcare Organizations: Handling patient funds typically requires fidelity coverage to protect against employee theft.
Understanding Surety Bonds
Definition and Purpose
Surety bonds are three-party agreements that guarantee performance or compliance with specific obligations. Unlike fidelity bonds, which operate as insurance policies, surety bonds create a guarantee that one party (the principal) will fulfill obligations to another party (the obligee).
These three-party contracts protect project owners against contractor default, ensuring that work gets completed or that businesses follow applicable laws and regulations. Surety bonds serve as a risk transfer mechanism in contractual relationships, providing financial protection when principals fail to meet their commitments.
Types and Applications
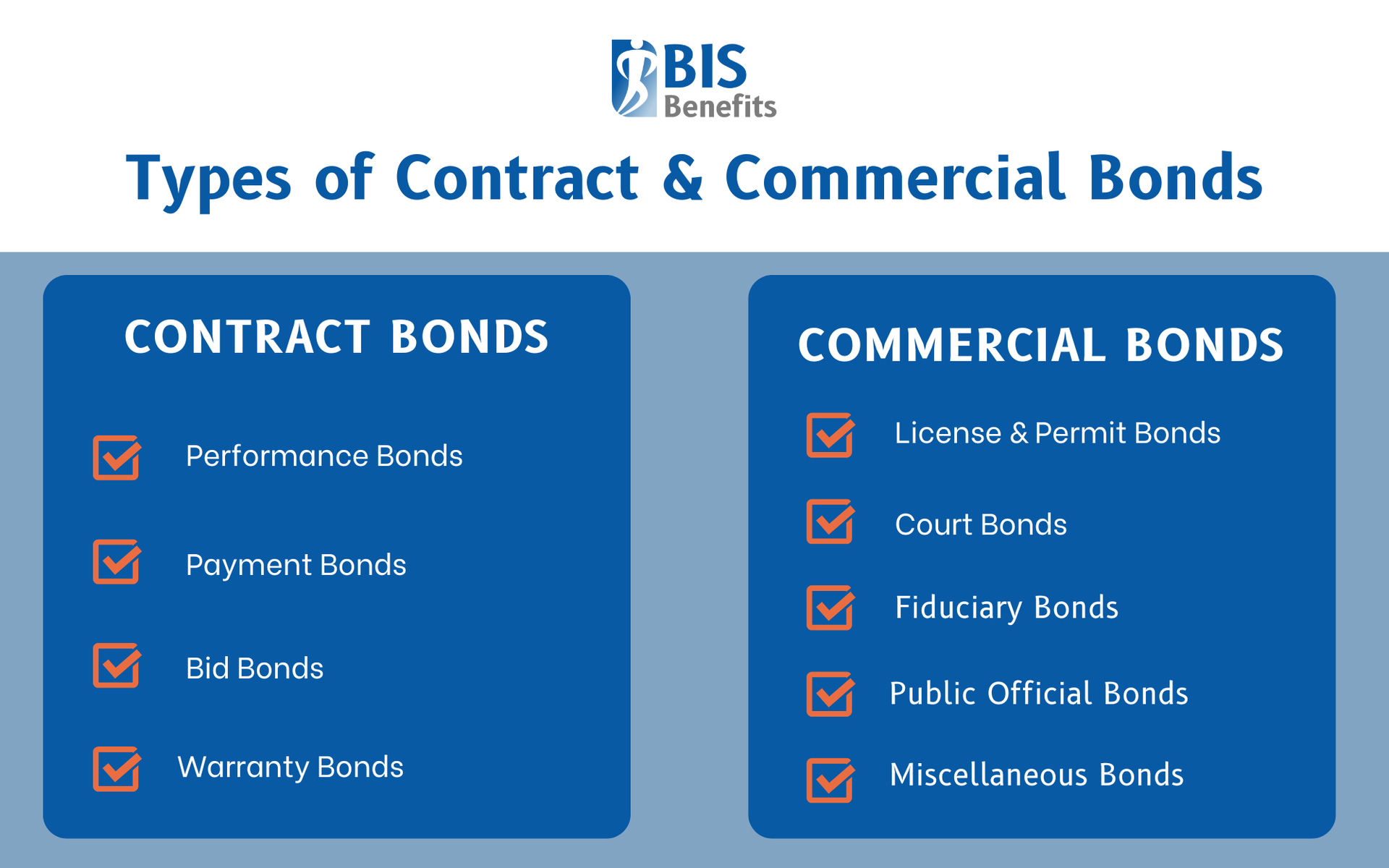
The surety bond landscape includes two primary categories-
Contract Bonds
Contract surety bonds include four main bond types-
- Performance Bonds: Performance bonds guarantee project completion in the event of a contractor’s default
- Payment Bonds: Payment bonds ensure that subcontractors and suppliers will be paid for labor and materials
- Bid Bonds: By guaranteeing contract execution, bid bonds financially protect the owner if the bidder fails to sign the contract or provide the required performance
- Warranty Bonds: Also called maintenance bonds, these bonds guarantee that any defects found in the original construction will be repaired during the warranty period
Commercial Bonds
There are five main types of commercial surety bonds-
- License and Permit Bonds: Required for certain types of business licenses, these guarantee that any work completed will be in compliance with state and local laws.
- Court Bonds: Also called judicial bonds, these are often needed for legal proceedings to protect from possible losses.
- Fiduciary Bonds: Also called probate bonds, these protect the wards, creditors, and heirs of a probate estate.
- Public Official Bonds: These guarantee that government employees will perform their duties according to the law.
- Miscellaneous Bonds: These cover specialized situations like utility bonds,customs bonds for importers and environmental compliance bonds.
Industries Requiring Surety Bonds
Business license requirements often mandate surety bonds as a condition of operation in regulated industries, such as-
- Construction: These projects commonly require performance and payment bonds.
- Mortgage Brokers: In many states, brokers must obtain surety bonds to protect clients and state regulators if the broker breaks the law.
- Court Proceedings: These may require bonds to guarantee payment of judgments.
The Three-Party Structure
For surety bonds, understanding the three-party relationship is crucial.
- Principal: The party required to obtain the bond, typically a contractor, business owner, or individual seeking a license.
- Obligee: The party protected by the bond, such as a project owner, government agency, or court.
- Surety: The insurance or bonding company providing the financial guarantee.
This structure distinguishes surety bonds from traditional insurance, as the surety expects to be reimbursed by the principal for any claims paid.
Key Differences Between Fidelity and Surety Bonds
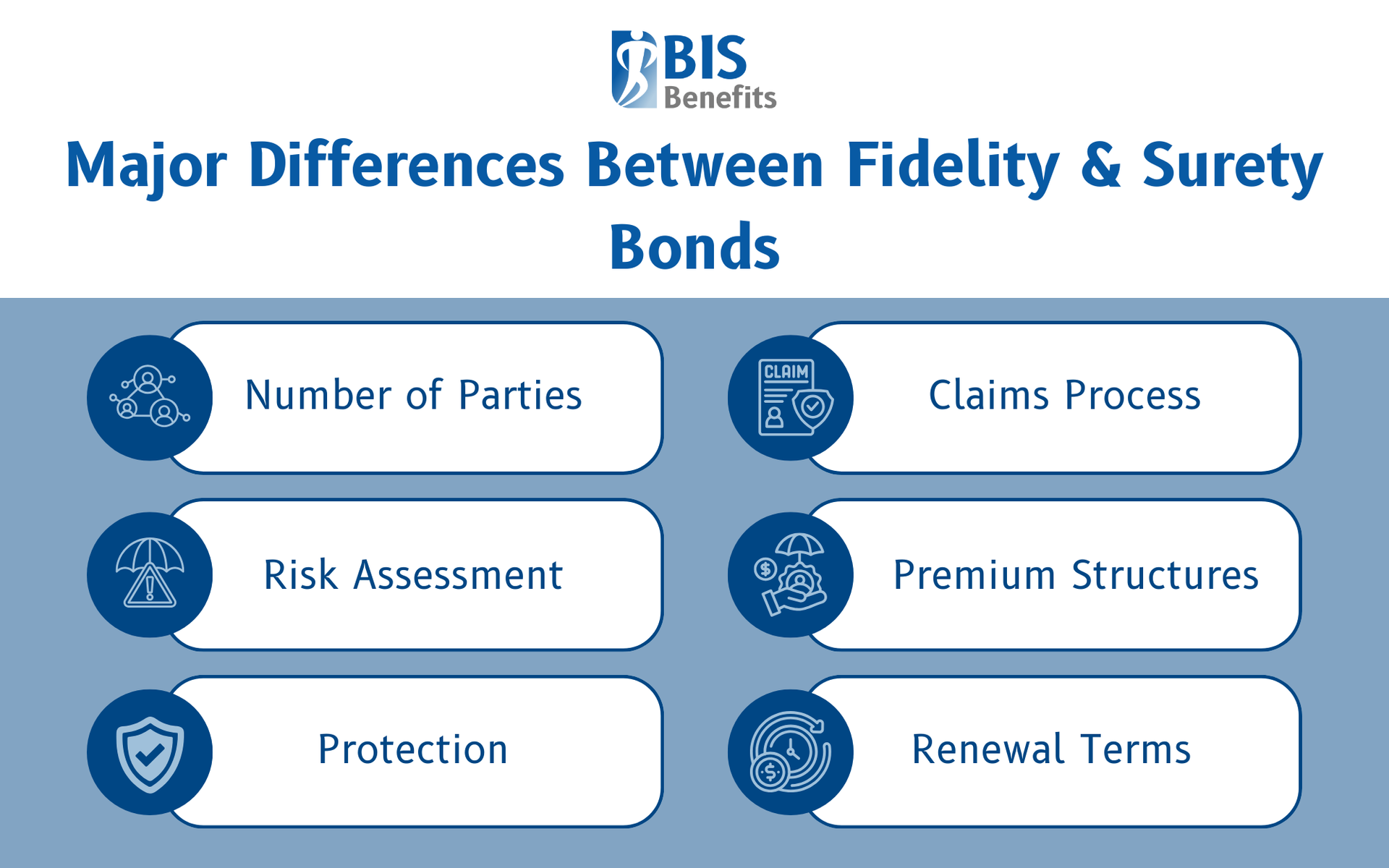
Number of Parties
This is the most fundamental difference between the two types of bonds. Fidelity bonds create a two-party agreement between the employer seeking protection and the insurance company. Surety bonds establish a three-party relationship involving the principal, obligee, and surety.
Protection
Fidelity bonds protect employers from their own employees' dishonest actions. Surety bonds protect third parties from the principal's failure to perform contractual obligations or comply with regulations.
Claims Process
Fidelity bond claims are filed directly by the employer with the insurance company, following traditional insurance procedures. Surety bond claims are filed by the obligee against the bond when the principal fails to perform. The surety investigates, potentially pays the claim, and seeks reimbursement from the principal.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment approaches differ based on what's being evaluated. Fidelity bond underwriting focuses on employee background checks and internal control systems. Surety bond underwriting examines the principal's financial capacity, industry experience, credit history, and project-specific risks.
Premium Structures
Premium structures reflect different risk models. Fidelity bond premiums are calculated based on coverage amounts, number of employees covered, deductible selections, and claims history. Surety bond premiums depend on the bond amount, the principal's credit score, project complexity, industry experience, and collateral requirements.
While they vary based on business size, contractor requirements, and risk factors, surety bonds typically range from
0.5% to 2% of the contract amount. Fidelity bonds have a similar range, costing between
1-3% of the total amount.
Renewal Terms
Fidelity bonds typically operate on annual renewal cycles with standard cancellation provisions. Surety bonds often run for project-specific terms and may be non-cancellable once issued, ensuring continuous protection throughout the bonded obligation's duration.

Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Fidelity Bond Requirements
Under state and federal law, fidelity bonding is required in specific situations-
- Employee Benefits Requirements: ERISA requires fidelity bonds for anyone handling employee benefit plan assets, with minimum coverage of 10% of plan assets
- Industry-Specific Mandates: These exist for businesses like banking institutions, securities dealers, and many government contractors handling public funds
- State Insurance Regulations: These impose bonding requirements for certain licensed professions
Surety Bond Requirements
- The Miller Act: These require performance and payment bonds on federal construction projects exceeding $150,000
- "Little Miller Acts": These state-level regulations impose similar requirements for state and local government projects
- Industry Licenses: Professional licensing boards across different industries mandate surety bonds as conditions for license issuance
- Courts Order Bonds: In litigation contexts, these guarantee payment of potential judgments
Compliance Considerations
Both bond types involve compliance obligations, including-
- Laws often specify minimum coverage amounts
- Regulatory bodies may require bonds from approved surety companies
- Renewal deadlines demand attention to ensure continuous coverage
- Regulatory reporting creates ongoing administrative responsibilities for bonded entities
Claims Process and Recovery
Fidelity Bond Claims
When employee dishonesty occurs, employers must discover the loss and report it promptly. After gathering evidence and documenting financial losses, the employer must cooperate with the insurer's investigation. Settlement occurs after the investigation confirms coverage, with the insurer paying valid claims and potentially pursuing recovery against the dishonest employee.
Surety Bond Claims
Surety bond claims begin when an obligee provides notice to all parties of the principal's failure to perform. The surety investigates and determines appropriate responses, which may include completing work through another contractor, paying the obligee for losses, or disputing invalid claims. The principal faces indemnification responsibilities, meaning they must reimburse the surety for any amounts paid on claims.
Recovery Challenges
Both bond types face many different recovery challenges, including-
- Proof of Loss: Claimants must provide adequate proof of loss. These requirements can be different by state.
- Time Requirements: Bond durations, renew requirements, and other limitations can restrict when claims can be filed.
- Subrogation Rights: Sureties and insurers maintain subrogation rights to recover paid claims from responsible parties.
- Financial Obstacles: Legal costs and collection efforts can make recovery expensive and time-consuming, especially when principals or dishonest employees lack assets.
Choosing the Right Bond Type
Proper bond selection starts understanding your potential financial exposure and determining appropriate coverage amounts.
- Identify whether you face internal risks from employee dishonesty or external risks from contractual non-performance
- Evaluate whether contractual obligations or regulatory requirements mandate specific bond types.
- Determine appropriate coverage amounts based on these findings
Working with experienced insurance agents and brokers who understand both fidelity and surety bonds ensures proper coverage selection. These professionals can compare coverage options and costs across carriers to make sure you receive adequate protection at competitive rates while meeting all legal and contractual bonding requirements.
Explore Commercial Insurance Bond Options with BIS Benefits
Understanding the differences between fidelity bonds and surety bonds is essential for protecting your business and meeting legal requirements. Fidelity bonds address internal risks from employee dishonesty, while surety bonds guarantee external obligations to third parties. Proper risk identification and coverage selection prevent costly gaps in protection.
BIS Benefits specializes in helping businesses navigate the complex world of
commercial bond insurance. Our experienced brokers assess your specific risks, explain your bonding options, and connect you with carriers offering competitive rates.
Request a Quote today to discuss your bonding needs and discover how BIS can protect your business with the right bond solutions.












